
NASA is set to launch a spacecraft to test whether it can deflect an asteroid away from a potentially catastrophic collision with Earth.
Fortunately this asteroid is not a threat to Earth – but scientists including Stephen Hawking have described impact events as among the greatest threats facing humanity.
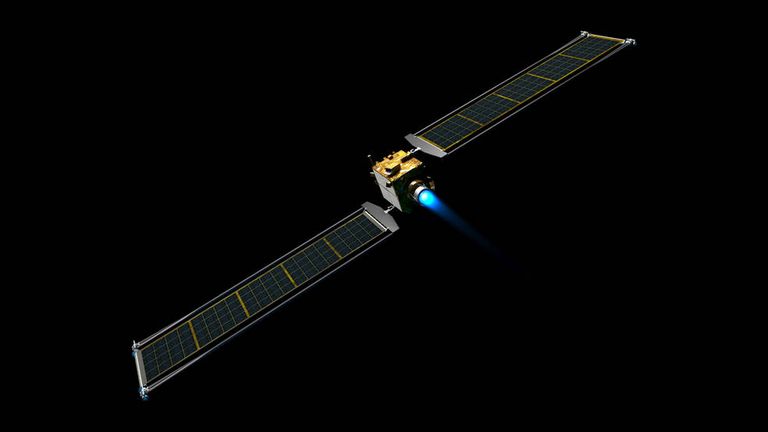
Take-off for the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission is scheduled for Tuesday and the spacecraft is attached to its payload adapter in SpaceX’s facility at the Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. It will be launched on top of a Falcon 9 rocket.
The DART spacecraft itself is roughly the size of a small car, and the mission is being supported by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory.
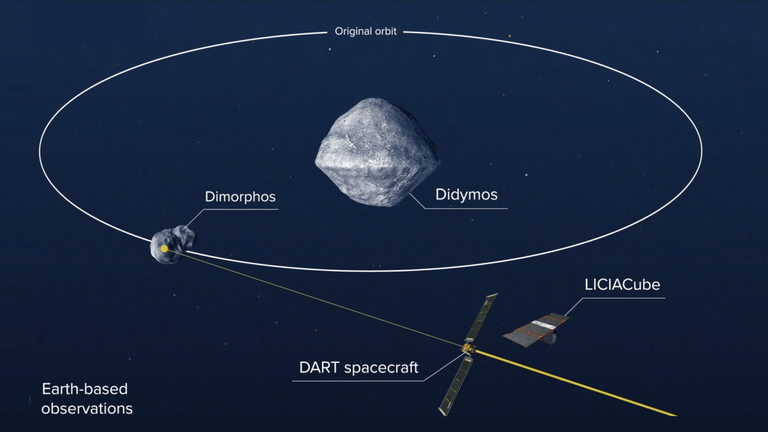
It will eventually slam into its much larger target and hopefully shift its orbit, all while being observed by the LICIACube satellite developed by the Italian space agency.
It will be the first-ever demonstration of the “kinetic impactor” technique to change the motion of an asteroid in space.
In the culmination of the $330m (£246m) mission, DART will smash into a near-Earth double asteroid known as Didymos and Dimorphos, with the latter being a “moonlet” estimated to be about 160 metres in size.
The plan will be for the small spacecraft to kinetically impact Dimorphos at a speed of roughly 6.6 kilometres per second and, in doing so, shorten its orbit about Didymos.
This nudge technique is preferred to blowing asteroids apart in the style of the film Armageddon, because the fragments from such an explosion could continue to imperil the planet.
A study from researchers at Johns Hopkins University in the US published in 2019 warned that for objects large enough to be targeted it was likely the blasted away fragments would reform under gravity.
Scientists say that no known asteroids larger than 140 metres in size have a significant chance of hitting the Earth within the next century.
However they warn only 40% of these asteroids have been found – and that much smaller asteroids could still cause enormous destruction.
This is because humanity’s detection systems are limited by physics – our ability to survey asteroids in the dark of space in our solar system depends on the direction of approach and the phase of the moon.
Small impactors are regularly detected just hours in advance, and the majority of asteroids that do hit Earth are from previously undiscovered objects.
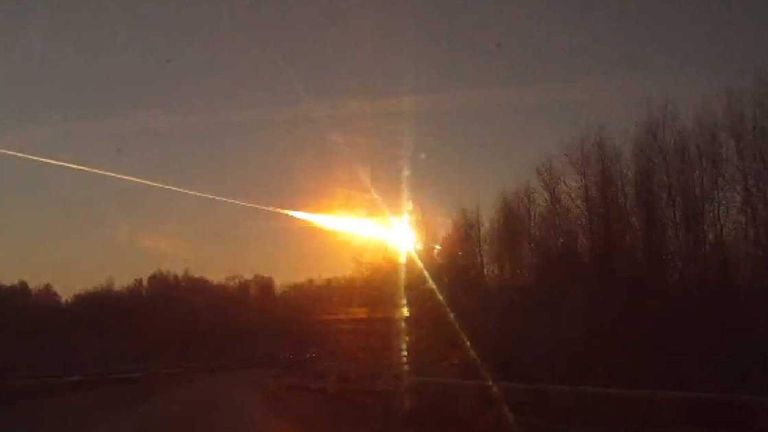
Back in 2013, a meteor exploded in the atmosphere near Chelyabinsk in Russia, causing an enormous fireball, shattering windows, and leading to potentially more than a thousand people to seek medical treatment for their indirect injuries.
That asteroid is believed to have been roughly 20 metres in size and was completely undetected before it entered the atmosphere, in part because it approached Earth from the direction of the sun.
It briefly outshone the sun and inflicted severe burns on observers below, as well as smashing windows and rattling buildings.
According to Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, the Chelyabinsk meteor created “an airburst and shockwave that struck six cities across the country - and [sent] a stark reminder that dangerous objects can enter Earth’s atmosphere at any time”.
“Astronomers estimate there are tens of thousands of near-Earth asteroids close to 500ft wide and larger, big enough to cause regional devastation if they actually hit Earth.
“The Chelyabinsk object was just about 60ft wide, demonstrating that even small asteroids can be of concern - and making real-world tests of space-based planetary defence systems all the more important,” the university added.






More Stories
5 Reasons Why Everyone Should Look Forward to Save Earth Mission’s Takeoff Event
Save Earth Mission’s Takeoff Event Countdown Starts: Get Ready to Witness History
The Save Earth Mission: A Global Movement Towards a Sustainable Future